Introduction to the Article

The Union Budget 2024-25 has brought several significant changes that directly impact salaried employees. From enhanced contributions to the National Pension System (NPS) to new income tax slabs and increased deductions, this budget aims to improve the financial well-being of employees. In this article, we will explore the key changes introduced in the budget and provide actionable steps for salaried employees to maximize their benefits.
The Union Budget 2024-25 has introduced significant changes that affect various sections of the population, including salaried employees, mutual fund investors, retirees, and the common man. This comprehensive guide will help you understand the key takeaways from the budget and provide actionable steps to optimize your financial planning. From enhanced NPS contributions to new tax regimes and investment opportunities, we cover everything you need to know to make informed decisions and maximize your benefits.
This year’s Union Budget 2024-25 is designed to create equal opportunities for all, particularly the poor (‘Garib’), women (‘Nari’), youth (‘Yuva’), and farmers (‘Annadata’). As India progresses towards becoming a developed nation by 2047, the budget aims to promote employment, support MSMEs, and empower the middle class. The overarching theme of the budget is ‘EMPLOYMENT,’ which stands for:
- E – Employment & Education
- M – MSMEs
- P – Productivity
- L – Land
- O – Opportunities
- Y – Youth
- M – Middle Class
- E – Energy Security
- N – New Generation Reforms
- T – Technology
I. Key Highlights of the Budget
Industrial Development:
- Development of ‘Plug and Play’ Industrial Parks in 100 cities with complete infrastructure.
- Establishment of 12 Industrial Parks under the National Industrial Corridor Development Programme.
Youth Employment and Skilling:
- Creation of employment opportunities for the youth.
- Financial support for domestic higher education loans up to ₹10 lakh.
- E-vouchers for 1 lakh students annually for a 3% interest subvention on loans.
- Skilling 20 lakh youth over five years.
- Upgrading 1,000 Industrial Training Institutes (ITIs) in hub and spoke arrangements.
- Revised Model Skill Loan Scheme facilitating loans up to ₹7.5 lakh with a government-guaranteed fund.
- Development of rental housing with dormitory-type accommodation for industrial workers.
Support for Street Vendors and Tourism:
- Development of 100 weekly ‘haats’ or street food hubs in select cities.
- Transformation of religious and tourist sites like Vishnupad Temple and Mahabodhi Temple in Bihar, and comprehensive development initiatives for Rajgir and Nalanda.
- Assistance for developing Odisha as a tourist destination.
Simplified tax regime for foreign shipping companies operating domestic cruises in India.
Fiscal Policies and Economic Reforms:
- Progressive fiscal deficit consolidation at 4.9%.
- Economic reforms to aid the capital market and address long-term capital gains.
- New tax regime income tax slabs and increased standard deductions.
- Enhanced deduction on family pension and increased employer contributions towards NPS.
- Increased capital gains exemption from ₹1 lakh to ₹1.25 lakh.
- Abolishment of angel tax to boost the startup ecosystem.
- Special schemes for MSMEs focused on easy access to credit.
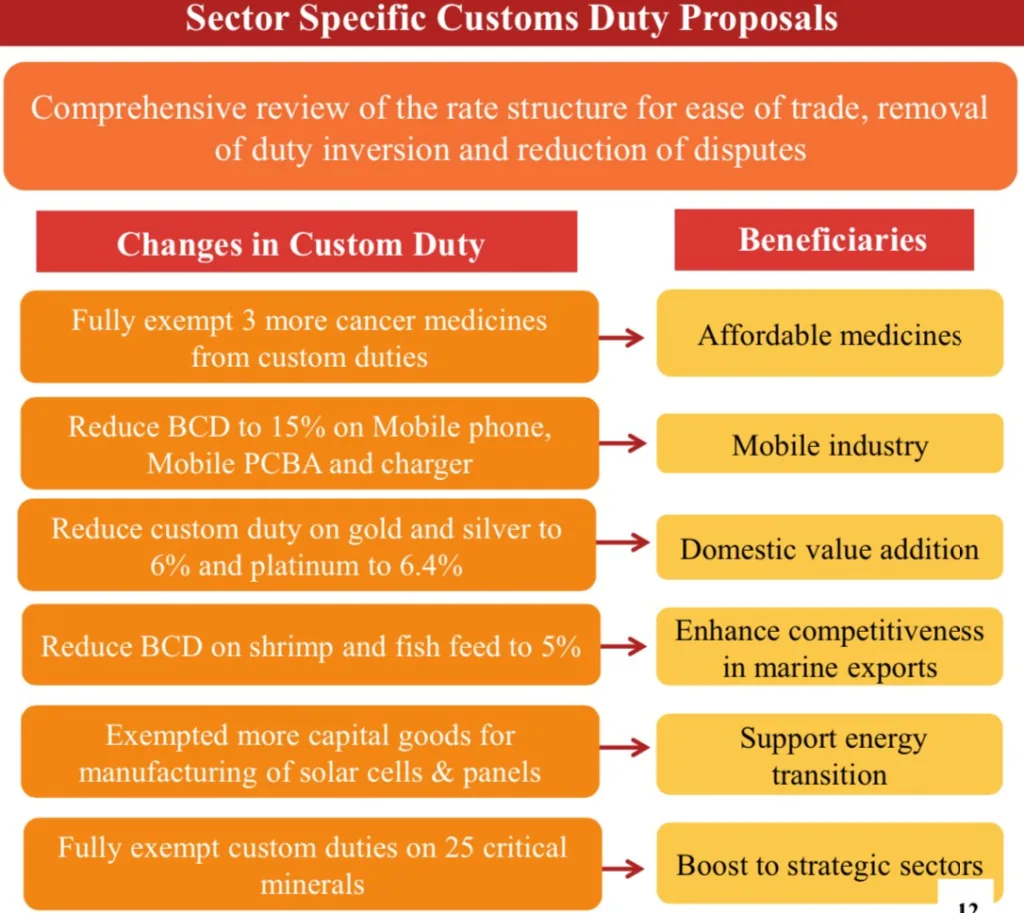
Healthcare and Custom Duty Adjustments:
- Removal of customs duty on three more medicines to aid cancer patients.
- Reduction of basic customs duty on mobile phones, PCBA, and chargers.
- Exemption of 25 critical minerals from customs duties.
- Expanded list of exempted capital goods for manufacturing solar cells and panels.
Corporate Tax and Gold Prices:
- Reduction of corporate tax rate on foreign companies from 40% to 35%.
- Potential drop in gold prices due to reduced import duty.
Energy and R&D Initiatives:
- Promotion of solar panel installations through the PM Surya Ghar Muft Bijli Yojana.
- Policy for promoting pumped storage projects for electricity storage.
- R&D partnerships for Small and Modular Nuclear Reactors.
Special Schemes and Infrastructure:
- Special finance schemes for Andhra Pradesh and Bihar under the Purvidya initiative.
- Continued focus on manufacturing, banking, and infrastructure development.
Real Estate and Non-Financial Assets:
- Abolition of indexation benefits for real estate and gold investments, considered a major negative.
Women’s Development:
- Allocation of ₹3 lakh crore for women’s and girls’ development.
II. Summary of Tax Changes
- Middle-Class Investor Taxes:
- Increased Security Transaction Tax on F&O from 0.01% to 0.02%.
- Security transaction tax: 0.1% on buy & sell.
- Dividend distribution tax: 15%.
- Long-term capital gains tax: 12.5%.
- Short-term capital gains tax: 20%.

- Withdrawal of 20% TDS on repurchase by mutual funds or UTI.
- Reduced TDS rate on e-commerce to 0.1%.
- Merging of two tax exemption regimes for charities into one.
- Increased Security Transaction Tax on F&O from 0.01% to 0.02%.
- New Tax Regime Changes:
- Increased standard deduction from ₹50,000 to ₹75,000.
- Revised tax slabs:
- ₹0-3 lakhs: Nil
- ₹3-7 lakhs: 5%
- ₹7-10 lakhs: 10%
- ₹10-12 lakhs: 15%
- ₹12-15 lakhs: 20%
- Above ₹15 lakhs: 30%

Conclusion
Overall, the Union Budget 2024-25 aims to foster inclusive growth and development across various sectors, with significant focus on employment, skilling, and supporting the middle class. The proposed reforms and fiscal policies are geared towards building a robust economy as India strides towards becoming a developed nation by 2047.
III. Implications of the Union Budget 2024-25 for the Common Man

- Infrastructure Development:
- Simplified Impact: Faster and improved roads, bridges, and railways mean less travel time and better connectivity for daily commuters and businesses.
- Inclusive Economic Growth:
- Simplified Impact: Economic growth will benefit all regions and communities, ensuring that opportunities are evenly spread across the country.
- Budget Detail: Efforts to formalize the economy through digital public infrastructure and a unified Goods and Services Tax (GST) system are aimed at creating a seamless market.
- Financial Sector Strengthening:
- Simplified Impact: Improved access to savings, credit, and investment options can help individuals manage their finances better and plan for the future.
- Budget Detail: Strengthening financial institutions and implementing tax reforms to widen the tax base.
- Inflation Management:
- Simplified Impact: Keeping inflation under control means that the prices of essential goods and services remain stable, making it easier for families to budget and save.
- Budget Detail: Proactive measures to manage inflation within a specific policy band.
- Women Empowerment:
- Simplified Impact: More opportunities for women in education, employment, and entrepreneurship lead to greater economic independence and societal progress.
- Budget Detail: Initiatives like Mudra Yojana loans and reservations in political bodies aim to empower women and increase their participation in the workforce.
- Support for Farmers (Annadata):
- Simplified Impact: Direct financial support and insurance schemes help farmers manage risks and ensure a stable income, contributing to food security.
- Budget Detail: Programs like PM-KISAN SAMMAN Yojana and PM Fasal Bima Yojana offer financial assistance and crop insurance to millions of farmers.
- Youth Empowerment (Amrit Peedhi):
- Simplified Impact: Enhanced educational and entrepreneurial opportunities for the youth can lead to better career prospects and innovation.
- Budget Detail: Initiatives such as the National Education Policy 2020, Skill India Mission, and PM Mudra Yojana provide training, loans, and support for young entrepreneurs.
- Housing for All (PM Awas Yojana):
- Simplified Impact: More affordable housing projects mean better living conditions for families, reducing homelessness and improving quality of life.
- Budget Detail: Continued focus on building millions of houses, particularly in rural areas, to meet growing demand.
- Social Justice:
- Simplified Impact: Ensuring fair access to resources and opportunities for all social groups helps reduce inequality and promotes social harmony.
- Budget Detail: Direct Benefit Transfer schemes and targeted welfare programs aim to uplift marginalized communities and reduce poverty.
- Rooftop Solarization and Free Electricity:
- Simplified Impact: Free electricity for up to 300 units per month from solar power helps households save money and promotes sustainable energy use.
- Budget Detail: The rooftop solarization initiative aims to provide significant annual savings and additional income through selling surplus electricity.
These points highlight how the Union Budget 2024-25 aims to create a more inclusive, sustainable, and prosperous India by addressing various aspects of economic and social development
Summary of the Union Budget 2024-25
The Union Budget 2024-25 focuses on fostering economic growth, ensuring social justice, and empowering various segments of the population, including women, youth, and farmers. Key initiatives include the development of infrastructure, support for MSMEs, and policies promoting employment and skilling. The budget emphasizes financial inclusion, inflation management, and sustainable energy use, with specific programs targeting affordable housing, social justice, and free electricity through rooftop solarization.
IV. Action Plan for the Common Man
- Leverage Financial Support and Loans:
- Action: Explore government-backed loan schemes for education and entrepreneurship.
- Benefits: Easier access to credit can help in pursuing higher education or starting a business.
- Utilize Skilling Programs:
- Action: Enroll in government-sponsored skilling programs to enhance employability.
- Benefits: Acquiring new skills can open up better job opportunities and career growth.
- Take Advantage of Tax Reforms:
- Action: Understand and utilize the new tax slabs and deductions.
- Benefits: Optimizing tax payments can result in significant savings and better financial planning.
- Invest in Sustainable Energy:
- Action: Install rooftop solar panels to benefit from free electricity and potential income from surplus power.
- Benefits: Reduces electricity bills and supports sustainable energy initiatives.
- Explore Affordable Housing Options:
- Action: Apply for affordable housing schemes under PM Awas Yojana.
- Benefits: Access to quality housing at lower costs can improve living standards.
- Participate in Social Welfare Programs:
- Action: Check eligibility and apply for Direct Benefit Transfer schemes and other welfare programs.
- Benefits: Financial assistance and subsidies can help manage daily expenses and improve quality of life.
- Support for Farmers:
- Action: Utilize programs like PM-KISAN SAMMAN Yojana and crop insurance schemes.
- Benefits: Ensures financial stability and protection against crop failures.
- Encourage Youth Participation:
- Action: Engage in educational and entrepreneurial opportunities provided by the government.
- Benefits: Better career prospects and support for innovation and startups.
- Monitor Policy Changes and Updates:
- Action: Stay informed about new policies and reforms affecting your sector.
- Benefits: Helps in making informed decisions and leveraging new opportunities.
V. Steps to Take Now

- Review Your Financial Goals: Align them with the new budget provisions, focusing on areas like education, housing, and sustainable energy.
- Plan for Education and Skilling: Identify courses and programs eligible for government loans and support.
- Evaluate Housing Options: Look into affordable housing schemes and their benefits.
- Install Solar Panels: If applicable, explore the feasibility of installing rooftop solar panels.
- Stay Informed: Regularly update yourself on budget-related news and policies to make the most of available benefits.
By taking these actions, individuals and families can better navigate the economic landscape shaped by the Union Budget 2024-25, ensuring a more secure and prosperous future.
VI. Implications of the Union Budget 2024-25 for Mutual Fund Investors

The Union Budget 2024-25 introduces several changes that will impact mutual fund investors. Key points include adjustments in capital gains tax rates, incentives for long-term investments, and alterations in the tax treatment of dividends and securities transactions.
Key Changes and Their Implications
- Capital Gains Tax Adjustments:
- Short-Term Capital Gains (STCG): The tax rate on STCG has increased from 15% to 20%.
- Implications: This change makes short-term investments less attractive due to higher tax outgo. Investors might consider holding their investments for a longer period to benefit from lower long-term capital gains tax rates.
- Long-Term Capital Gains (LTCG): The exemption limit for LTCG has increased from ₹1 lakh to ₹1.25 lakh.

- Implications: Investors can now realize more gains without incurring tax. This encourages long-term investment, which aligns with wealth-building strategies.
- Tax Treatment of Dividends:
- Dividend Distribution Tax (DDT): The rate remains unchanged at 15%.
- Implications: Investors in dividend-paying mutual funds will continue to see a 15% tax on dividends, impacting net returns from dividend-focused funds.
- Security Transaction Tax (STT):
- STT on F&O (Futures & Options): Increased from 0.01% to 0.02%.
- Implications: Higher transaction costs for trading in F&O segments might deter frequent traders, pushing them towards more traditional investment avenues.
- Simplification of Income Tax Act:
- Consolidation and Simplification: Efforts to make the Income Tax Act more concise and easier to understand.
- Implications: Investors will find it simpler to comply with tax laws and better understand their tax obligations, aiding in more efficient financial planning.
Suggested Actions for Mutual Fund Investors
- Review Investment Horizons:
- Action: Reassess your investment strategy, focusing on long-term holdings to minimize the impact of higher STCG rates.
- Benefits: Holding investments for longer periods reduces the tax burden and aligns with long-term wealth creation goals.
- Utilize the Increased LTCG Exemption:
- Action: Plan to utilize the ₹1.25 lakh exemption limit for LTCG. Schedule redemptions to stay within this limit where possible.
- Benefits: Maximizing the use of this exemption can significantly enhance after-tax returns.
- Consider Tax-Efficient Funds:
- Action: Explore tax-efficient mutual funds, such as Equity Linked Savings Schemes (ELSS), which offer tax benefits under Section 80C.
- Benefits: These funds provide tax deductions and can reduce overall tax liability.
- Monitor Dividend Policies:
- Action: Be mindful of the tax implications of dividends. Consider growth options over dividend options in mutual funds to avoid the 15% DDT.
- Benefits: Opting for growth funds can improve net returns as the gains are only taxed upon redemption and benefit from LTCG exemptions.
- Stay Informed on STT Changes:
- Action: Factor in the increased STT costs when trading in F&O segments and consider adjusting your trading frequency accordingly.
- Benefits: Understanding the cost implications helps in maintaining profitability and optimizing trading strategies.
- Leverage Professional Advice:
- Action: Consult with a financial advisor or tax consultant to navigate the changes effectively and optimize your investment strategy.
- Benefits: Professional guidance ensures you make informed decisions that align with your financial goals and tax situation.

By taking these actions, mutual fund investors can better adapt to the changes introduced in the Union Budget 2024-25, ensuring their investment strategies remain robust and tax-efficient.
VII. Implications of the Union Budget 2024-25 for Salaried Employees

The Union Budget 2024-25 brings several changes that directly impact salaried employees, including adjustments to the National Pension System (NPS), income tax changes, and the new tax regime. Here’s a detailed look at these changes and suggested actions for salaried employees.
Key Changes and Their Implications
- Increase in NPS Employer Contribution:
- Change: The employer’s contribution to the NPS has increased from 10% to 14% of the employee’s salary.
- Implications: This change enhances retirement savings for employees, making the NPS a more attractive retirement planning tool. The increased contribution from the employer boosts the overall corpus without additional cost to the employee, leading to higher retirement benefits.
- Income Tax Changes:
- Change: The new tax regime has introduced changes to the tax slabs and increased the standard deduction.
- Standard Deduction: Increased from ₹50,000 to ₹75,000.
- Benefit: This provides additional relief to salaried employees, reducing taxable income and increasing take-home pay.
New Tax Slabs:
- ₹0-3 lakhs: Nil
- ₹3-7 lakhs: 5%
- ₹7-10 lakhs: 10%
- ₹10-12 lakhs: 15%
- ₹12-15 lakhs: 20%
- Above ₹15 lakhs: 30%
Benefit: The realignment of tax slabs offers potential tax savings for many salaried employees, particularly those with lower to middle incomes.
- Enhancement in Family Pension Deduction:
Change: Deduction on family pension increased from ₹15,000 to ₹25,000 under the new regime.
Implications: This increase provides additional tax relief to pensioners, enhancing their disposable income.
- Deduction of Employer’s NPS Contribution:
Change: Deduction of expenditure by employers towards NPS increased from 10% to 14% of the employee’s salary.
Implications: This encourages more significant employer contributions to NPS, resulting in a higher accumulation of retirement funds for employees.
Suggested Actions for Salaried Employees
- Maximize NPS Contributions:
Action: Take full advantage of the increased employer contribution to NPS by ensuring you are enrolled in the scheme. Consider making additional voluntary contributions to maximize the benefits.
Benefits: Enhanced retirement savings and additional tax benefits under Section 80CCD(1B).
- Utilize the Standard Deduction:
Action: Ensure that the increased standard deduction is factored into your tax planning.
Benefits: Reduces taxable income, leading to lower tax liability and increased take-home pay.
- Review and Opt for the Most Beneficial Tax Regime:
Action: Compare the old and new tax regimes to determine which offers the most tax savings based on your income and deductions.
Benefits: Optimizing tax liability by choosing the regime that provides the maximum benefit based on your financial situation.
- Plan for Family Pension Benefits:
Action: If you are eligible for family pension, ensure you claim the enhanced deduction.
Benefits: Increased tax relief, resulting in higher disposable income for pensioners.
- Leverage Employer NPS Contributions:
Action: Encourage your employer to contribute the maximum 14% to your NPS account. Additionally, consider your own contributions to boost retirement savings.
Benefits: Maximizes retirement corpus and avails tax benefits under Section 80CCD.
By taking these actions, salaried employees can effectively leverage the changes introduced in the Union Budget 2024-25, ensuring better financial planning, optimized tax savings, and enhanced retirement benefits.
VIII Plus and Minus of the Budget

Positives:
- Increased Capital Expenditure: The budget focuses on enhancing capital spending, which is set to grow by 17%, driving infrastructure and development projects.
- Tax Reforms for Middle Class: Introducing tax breaks and restructuring tax slabs to increase disposable income, aiming to boost consumption.
- Support for EV and Renewable Industries: Proposals for reducing GST on EV components and aligning them with renewable energy initiatives.
Negatives:
- Slow Growth in Corporate Tax: Despite high corporate earnings, the growth in corporate tax has been modest, indicating potential challenges in revenue collection.
- High Debt Servicing Costs: An increase in debt servicing costs could strain fiscal resources, impacting the budget’s sustainability.
Cost Implications
Likely to Become Costlier:
- Products with reduced subsidies or where GST reductions are not implemented might see a price increase.
Likely to Become Cheaper:
- Electric vehicles and related components might become cheaper if the proposed GST reductions are enacted.
Written by Taresh Bhatia
Taresh Bhatia is a Certified Financial Planner and Coach at the Richness Academy. With years of experience in guiding clients towards financial freedom and a rich, fulfilling life, Taresh specializes in helping diverse groups, including young married couples, senior executives, entrepreneurs, retirees, single mothers, and divorced women. He is also the author of the Amazon best-seller, “The Richness Principles.”
Disclaimer
The information provided in this article is for general informational purposes only and should not be construed as financial advice. While every effort has been made to ensure the accuracy of the information, it may not apply to your individual circumstances. Always consult with a qualified financial advisor before making any financial decisions. Taresh Bhatia and the Richness Academy are not responsible for any financial losses or damages incurred as a result of following the advice provided in this article.
The author of this article, Taresh Bhatia, is a Certified Financial Planner® and advocate for female empowerment. For more information and personalized financial guidance, please contact taresh@tareshbhatia.com
He has authored an Amazon best seller-“The Richness Principles”. He is the Coach and founder of The Richness Academy, an online coaching courses forum. This article serves educational purposes only and does not constitute financial advice. Consultation with a qualified financial professional is recommended before making any investment decisions. An educational purpose article only and not any advice whatsoever.
©️2025: All Rights Reserved. Taresh Bhatia. Certified Financial Planner®
Subscribe Now for Upcoming Blogs!
[convertkit form=6555951]
📢 Join free live webinar —
Couple Finance Formula™ Register here




